AESTHETIC SURGERY
Breast augmentation
Breast augmentation

Surgical approach
"Mini-incision" technique
In the "mini-incision" technique taught by Dr. Fanous, a small incision is made under the breast using fine instruments. The breast prosthesis is inserted by Dr. Fanous under four muscles (rather than one) to give the implant more support. As a result, breast tissue is minimally disturbed and the small incision scar can be better concealed. In the future, as the implant is placed under several muscles, it is normal for it to move when these muscles contract.
(514) 935-9906

Surgery details
Breast implants are usually inserted during a surgical procedure, for which there are three classic types of incision:
- infra-mammary incision (technique used by Dr Fanous);
- peri-areolar incision or;
- transaxillary incision.
These three incisions enable the prosthesis to be placed under a muscle, or under 4 muscles (Dr. Fanous' technique), or under the gland (between the muscle and the breast tissue). Breast augmentation takes about an hour and a half.
Anesthesia... without general anesthesia
Local anesthesia with sedation is used for your breast augmentation. Therefore, breast plastic surgery is performed by Dr. Fanous without the need for general anesthesia. You can go home the same day as your breast augmentation.
After breast surgery
Recovery time
Recovery time varies from person to person, but you should be able to resume many of your regular activities after about a week.
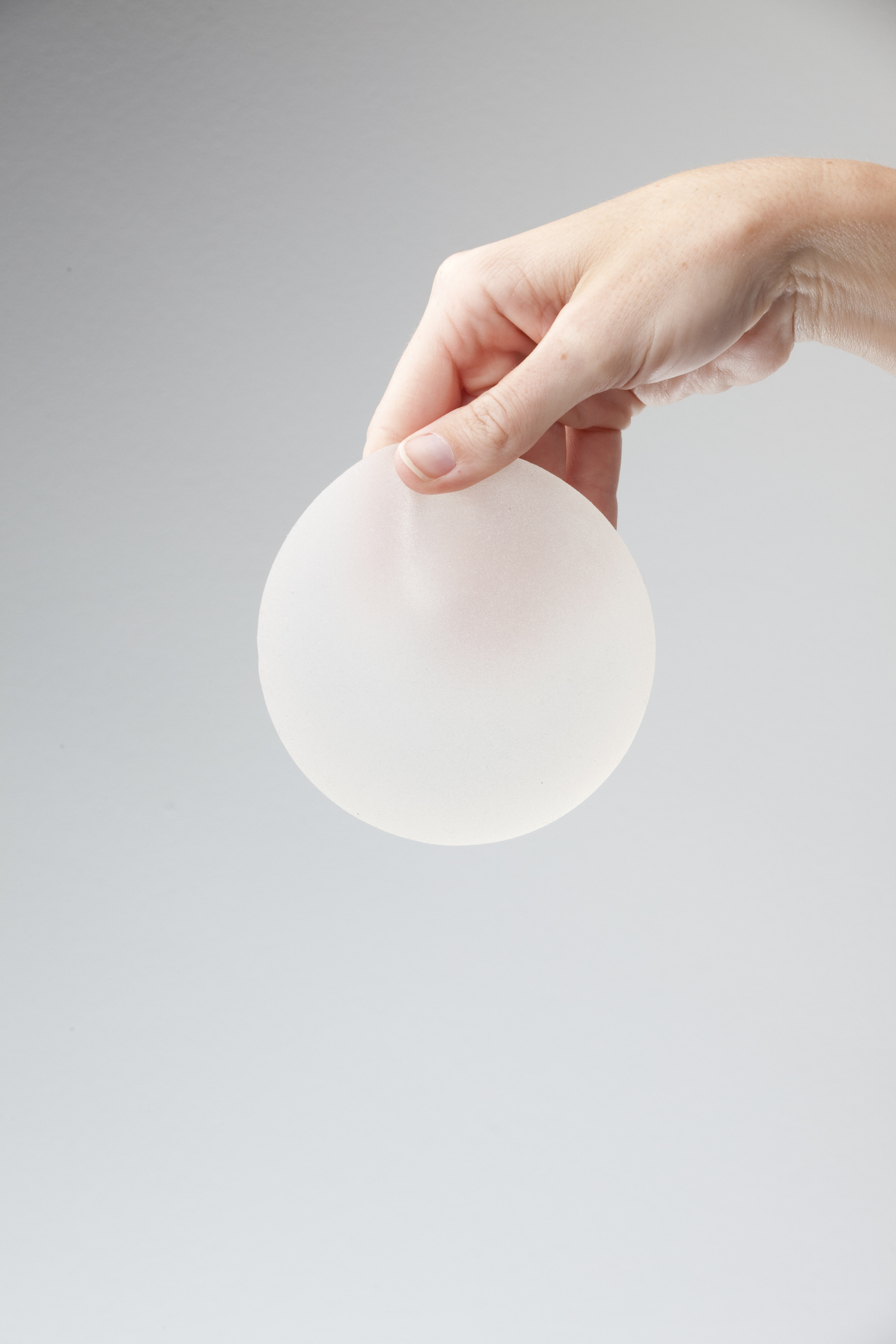


Breast implants
Breast implants
Mammary prostheses (breast implants) are made of a flexible outer envelope containing either a saline liquid (saline) or a silicone gel (cohesive gel).
Saline is very similar to the fluid that makes up 70% of the human body. If the prosthesis breaks and the saline escapes, it is safely absorbed by the body.
Silicone gel has a slightly softer consistency than saline, but requires a longer incision.
(514) 935-9906
(514) 935-9906
(514) 935-9906
(514) 935-9906
Breast augmentation
Breast anatomy
The breast is composed of adipose tissue, glandular tissue and fibrous connective tissue. Inside the breast are blood vessels, milk ducts, fat, glands and sensory nerves. The breast is enveloped by a layer of adipose tissue that gives it its supple consistency and shape. Under the breast are the muscles that contribute to arm movement.
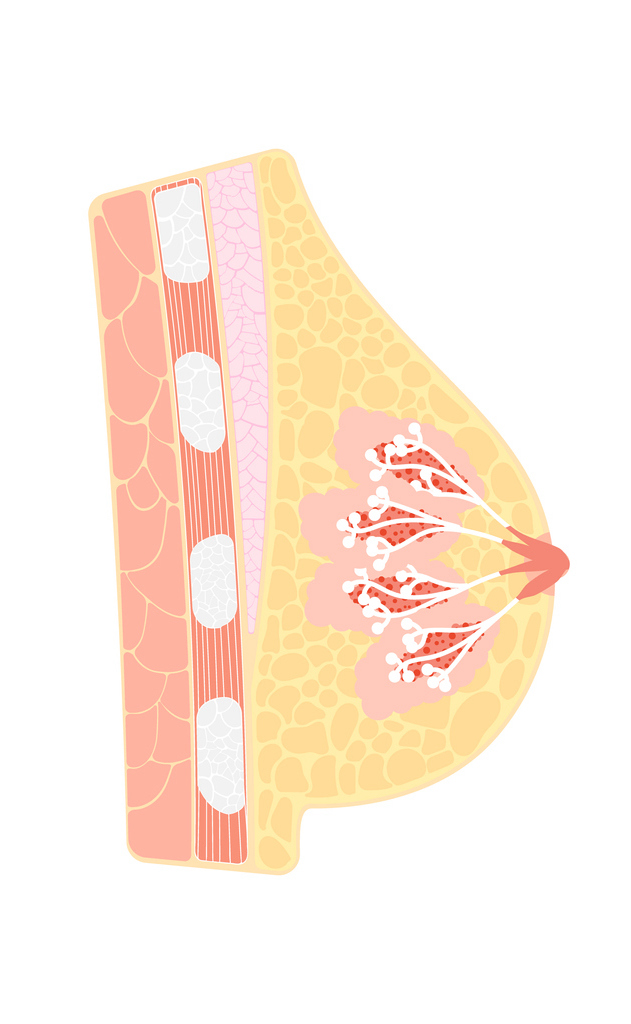

Breasts vary considerably from one woman to another, both in size and shape. The volume and shape of your breasts are determined by the amount of breast tissue and adipose tissue they contain. Their volume also depends on factors such as age, previous pregnancies, genetic make-up and skin elasticity.
After surgery
After surgery, the two breasts may be slightly different from one another. Such variations in volume and shape are normal and occur in most women.

Risks
Possible complications
As with any other aesthetic surgical procedure, complications of breast augmentation are possible but not frequent: deflation, infection, hematoma, prolonged healing, capsular contracture, displacement of the prosthesis, altered sensitivity of the nipple and breast, more difficulty in detecting tumors, calcium deposits in the tissue surrounding the prosthesis, need for additional surgeries, muscle weakness, nerve weakness, skin necrosis, stretch marks, and so on.
The body's reaction to breast implants
The body produces a fibrous tissue made of collagen on the surface of the implant: this is known as the capsule. The formation of a capsule is a reaction that normally follows the installation of any prosthesis. In some women, the capsule may contract, causing a phenomenon known as 'capsular contracture' (fibrous capsule). This phenomenon results in hardening of the breast (induration), and may also cause discomfort or deformity. Some implants deflate or rupture within the first few weeks of implantation. Yet others remain intact 10 years or more after surgery. It is not known when deflation is most likely to occur.
Breast lift
Patients with breast ptosis (drooping breasts) may also opt for mastopexy (redraping) during breast augmentation. Mastopexy is a surgery used to pull the nipple upwards. Incisions are made around and below the nipple.

The costs
How much does breast augmentation cost?
To get a rough idea of the costs of a breast augmentation and to get answers to your other questions, please contact us today at 514-612-5991. We'd be delighted to discuss everything with you.
Depending on the aesthetic problem and the surgeon's reputation, the cost of surgery varies enormously.







